LIQUEN ESTRIADO Y NEVIL ?
NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL !!!
LICHEN STRIATUS AND ILVEN?
INFLAMMATORY LINEAR VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS !!!
EDITORIAL ESPAÑOL
==================
Hola amigos de la red DERMAGIC EXPRESS hoy te va hablar de un tema
bastante controversial y discutido hoy día, LA LESIONES
LINEALES en los NIÑOS, específicamente el NEVIL cuyas siglas
significan
NEVUS
EPIDÉRMICO
VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL, algunos científicos lo denominan
LIQUEN ESTRIADO, otros consideran que son entidades diferentes.
Para aclarar esta controversia vamos a explicar cada una de ellos
por separado, su HISTORIA, ETIOLOGÍA, EVOLUCIÓN, DIAGNÓSTICOS DIFERENCIALES y
TRATAMIENTOS:
1.) LIQUEN ESTRIADO:
A.) HISTORIA:
- Esta patología fue descrita inicialmente en 1898 por dos
dermatólogos franceses:
François Henri Balzer y
Lucien Marie François Mercier
quienes le dieron el nombre de
"trophoneurose lichenoid" en
casos lineales infantiles.
- Posteriormente en 1941, dos dermatólogos estadounidenses:
Francis Eugene Senear, y William Harry Caro, le dieron el nombre definitivo de
"lichen striatus" (liquen estriado),
estandarizándolo clínicamente.
B.) ETIOLOGÍA:
- La causa es desconocida (idiopática), por lo general encuentras
como antecedentes, LESIONES NEVICAS (LUNARES) en los
ascendientes del afectado.
- Como teoría principal de la aparicion del LIQUEN ESTRIADO
se postula un mecanismo denominado
MOSAICISMO GENÉTICO, mas un
DESENCADENAN TE AMBIENTAL, que activa clones de células cutáneas anómalas, en las
líneas de Blaschko, generando una respuesta inflamatoria T-celular, provocando una
migración de queratinocitos hacia esas LINEAS DE BLASCHKO, con la consecuente aparición de las lesiones.
"LAS LINEAS DE BLASCHKO: Son patrones cutáneos invisibles que representan trayectorias de una migración clonal de células epidérmicas que ocurre durante el desarrollo embrionario (semanas 6-8 de gestación). Son lineas imaginarias producto de un MOSAISCIMO GENÉTICO POSTZIGOTICO que siguen la proliferación de DOS poblaciones celulares formando configuraciones dependiendo del area del cuerpo, y no corresponden a dermatomas, ni a vasos linfáticos. Resumiendo es una migración celular embrionaria."
- En S: en el abdomen.
- En V: en la espalda.
- En forma espiral: Tronco.
- Lineales curvas: brazos y piernas.
- Estas Lineas fueron descritas por vez primera en 1901, por el Dermatólogo Alemán Alfred Blaschko en el VII Congreso de la Sociedad Dermatológica Alemana, donde presento 140 casos de lesiones lineales.
LINEAS DE BLASCHKO
En estas lineas IMAGINARIAS, es donde se expresan o manifiestan el LIQUEN ESTRIADO, EL NEVUS VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL (NEVIL), y otras patologías lineales como LA PSORIASIS LINEAL, el LIQUEN PLANO LINEAL, el VITILIGO SEGMENTARIO, y otras como la INCONTINENCIA PIGMENTARIA.
"EL DERMATOMA: Es un área específica de piel inervada sensorialmente por un solo nervio espinal (raíz dorsal de un segmento medular), ejemplo el CLÁSICO HERPES ZOSTER (NO LINEAL) y el HERPES SIMPLE RECIDIVANTE."
- FACTORES DESENCADENANTES IDENTIFICADOS:
en un 20 a 50% de los casos se han identificado, como
desencadenantes:
a.- Traumatismos menores:
El cual desencadenaría el fenómeno isomorfico de Koebner):
15%.
b.- Infecciones virales (varicela-zóster, EBV, CMV): 30%.
c.- Dermatitis atópica predisponente: 50-61%: historia personal o familiar.
e.- Vacunaciones: aspecto dudoso.
f.- Estrés, medicamentos, y dermatitis por contacto: Raros.
b.- Infecciones virales (varicela-zóster, EBV, CMV): 30%.
c.- Dermatitis atópica predisponente: 50-61%: historia personal o familiar.
e.- Vacunaciones: aspecto dudoso.
f.- Estrés, medicamentos, y dermatitis por contacto: Raros.
C.) CARACTERÍSTICAS CLÍNICAS :
- Se trata de una afección dermatológica rara que se presenta
predominantemente en niños de 4 años en adelante, con promedio entre 1 a
6 años; yo lo he visto aparecer en niños con pocos meses de nacido.
- Se presenta tanto en varones como hembras, con un predominio en
varones 2:1 sobre las niñas.
- Básicamente la lesión está caracterizada por la aparición ESPONTANEA de pápulas planas y placas cuyo color puede variar entre
hipocromía (sin color) o rosadas y en algunos casos hiperpigmentadas,
algunas de aspecto verrugoso, las cuales por cambios de temperatura se
"notan" mas.
- Estas van extendiéndose en forma "LINEAL" siguiendo una metamera de la piel, denominadas LINEAS DE BLASCHKO, hasta formar una especie de "CAMINO" o trayecto lineal, completamente asintomático o levemente
pruriginoso, el cual Puede presentarse en cuello, brazos, piernas, abdomen, área peri-anal, peri-vulvar, y en
algunos casos la cara.
- En algunos casos cuando el LIQUEN ESTRIADO cuando afecta la punta del dedo puede haber afectacion ungueal: onicolisis, onocomadesis, deshilachado. Esto se presenta solo en un 5% de los casos, y por lo general se resuelven las lesiones espontaneamente o con esteroides topicos.
- La mayoría son
totalmente asintomáticas
pero en algunos casos el único síntoma existente es el prurito o comezón
y constituyen un verdadero dolor de cabeza, para los padres de estos
niños que manifiestan esta condición, principalmente por el
aspecto estético.
"Los padres que van a la consulta creen que se trata de una "CULEBRILLA" por el aspecto lineal de la lesión, y una vez explicado el caso, quedan TOTALMENTE SORPRENDIDOS de que este tipo de enfermedad exista en la dermatología"
D.) EVOLUCIÓN:
El LIQUEN ESTRIADO en su evolución, es
AUTO-LIMITADO: El inicio por
lo general es agudo comienza a aparecer en días, con un pico de 1-3
meses, hasta que se detiene la aparición de las lesiones.
- Luego comienza la resolución la cual es
ESPONTANEA, y puede durar entre 6-12 meses (media 9 meses), dejando en
algunos casos
hipopigmentación
residual (28%), o
hiperpigmentación (8%), la cual desaparece en 1-2 años. El tiempo de resolución
disminuye si se aplican tratamientos adecuados.
- La patología raramente recidiva o recae: se dice que un 10% de los
casos; particularmente
NO HE VISTO RECAÍDAS en
estos casos.
E.) TRATAMIENTOS:
Hay varias opciones de tratamiento, que incluyen:
B.- Tacrolimus.
C.- Pimecrolimus.
D.- Calcipotriol.
E. Ttriamcinolona.
F.- Tazaroteno.
G.- Urea.
H. Ácido salicílico.
EL CLÁSICO LIQUEN ESTRIADO: DESAPARECE con un buen tratamiento dermatológico y un buen porcentaje (70%)
espontáneamente.
G.) DIAGNÓSTICOS DIFERENCIALES:
Existe una gran controversia con respecto a estas LESIONES LINEALES en
los niños y adultos y voy a tratar de explicártelo lo mejor posible: Las
mas comunes son:
1.) EL NEVIL O NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL:
A.) HISTORIA:
- Esta patología fue descrita
por primera vez en 1894 por el
dermatólogo
Aleman Paul Gerson Unna, uno de
los pioneros de la histopatología cutánea, quien identificó
características psoriasiformes en nevus epidérmicos lineales.
- En 1971, dos dermatologos
estadounidenses: Altman y Mehregan, definieron el término
"NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL (NEVIL)"
tras serie de 25 casos, diferenciándolo por inflamación intensa, de
otras patologías entre ellas el
LIQUEN ESTRIADO.
B.) ETIOLOGÍA:
NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL (NEVIL o ILVEN en inglés), tiene etiología similar al LIQUEN ESTRIADO: Se trata de un MOSAICISMO GENETICO, caracterizado por mutaciones postzigóticas en los QUERATINOCITOS durante embriogénesis (semanas 6-8), lo cual provoca una proliferación clonal hamartomatosa, mas una inflamación crónica. El cromosoma alterado es el 15q.
- No es hereditario en el 99% de los casos, considerándose de aparición adquirida esporádica, aunque han sido reportado algunos casos familiares (madre-hija).
- Como factores desencadenantes se han reportado: trauma local y HIV.
C.) CARACTERÍSTICAS CLÍNICAS:
- Es exactamente igual en presentación y características al LIQUEN ESTRIADO, de hecho hay científicos como lo mencione al principio que consideran ambas la misma enfermedad con diferente expresión clínica.
C.) CARACTERÍSTICAS CLÍNICAS:
- Es exactamente igual en presentación y características al LIQUEN ESTRIADO, de hecho hay científicos como lo mencione al principio que consideran ambas la misma enfermedad con diferente expresión clínica.
- Se presenta en niños y adolescentes entre 5 y 15 años y se han descrito casos de presentación en adultos (5%); el 75% de los casos se presenta antes de los 7 años. Un 15% se presenta entre el 1er año de vida y los 5 años.
- Algunos autores consideran la patología de índole congénita.
- Es considerado una variante del NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO, y muy SIMILAR en presentación al LIQUEN ESTRIADO, porque al igual que este, sigue las LINEAS DE BLASCHKO. y los sitios de aparición del mismo son las del Liquen Estriado: cuello, brazos, piernas, abdomen, área peri-anal, peri-vulvar, y en
algunos casos la cara.
D.) EVOLUCIÓN:
La evolución del NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL (NEVIL) es crónica y progresiva, comenzando en infancia precoz y persistiendo indefinidamente sin remisión espontánea, las lesiones verrugosas persisten y se necesita tratamiento para disminuir su apariencia, o hacerlas desaparecer.
- Hay casos de NEVIL donde las papulas o placas verrugosas NO EXISTEN, pero lo que le da la característica de NEVUS INFLAMATORIO LINEAL es que las lesiones SIN tratamiento NO DESAPARECEN, no hay regresión espontanea. Quedan lesiones hipo-pigmentadas, hiperpigmentadas o acrómicas de por vida.
- Esta es una de las GRANDES diferencias con EL LIQUEN ESTRIADO, el cual si presenta REMISIÓN ESPONTANEA.
E.) TRATAMIENTOS:
A.) Corticosteroides tópicos (40%): poca efectividad.
B.) Calcipotriol: (70%): control parcial.
C.) LASER CO2: (85%): ablación definitiva.
D.) Retinoides sistémicos (60%): poco uso, solo aclara las lesiones.
F.) RESUMEN:
Tanto el LIQUEN ESTRIADO como el NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL (NEVIL), son muy similares en cuanto a aparición y características clínicas, pero la gran diferencia entre ambas patologías, es lo que ya comentamos. EL LIQUEN ESTRIADO presenta en la gran mayoría de los casos con o sin tratamiento RESOLUCIÓN ESPONTANEA, el NEVUS VERRUGOSO EPIDÉRMICO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL, no presenta REMISIÓN ESPONTANEA, perdura toda la vida, a menos que se haga tratamiento, Y AUN ASÍ, puede que queden marcas residuales.
- Algunos autores consideran ambas patologías una misma ENTIDAD con expresión clínica diferente.
- Algunos científicos han descrito desaparición TOTAL de NEVIL con tratamientos tópicos; este hecho plantea la gran interrogante ? eran LIQUEN ESTRIADOS ??
- Aquí te voy a decir algo basado en MI EXPERIENCIA: EL LIQUEN ESTRIADO, considerado por algunos científicos como una variante del NEVIL (NEVUS VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL), cuando desaparece con un buen tratamiento
dermatológico, o espontáneamente, NO VUELVE A APARECER. JAMAS he visto un LIQUEN ESTRIADO que se curó, volver a presentarse, o recidivar.
NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO INFLAMATORIO LINEAL
EL NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO LINEAL: (NO INFLAMATORIO):
Se trata del CLÁSICO NEVIL: una lesión NEVICA, tipo lunar en LINEA de aspecto VERRUGOSO, (ver foto), su coloración es pardo
claro o hiperpigmentada. Como dijimos previamente, la gran diferencia es que
este NO DESAPARECE con tratamiento tópico convencional y persiste hasta edad
adulta. Hay que recurrir a otros métodos como la extirpación
quirúrgica o laser, la mayoría de ellos son congénitos o aparecen
en la infancia.
NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO VERRUGOSO LINEAL DORSO DE MANO
DIAGNOSTICO DIFERENCIAL
CON OTRAS PATOLOGÍAS CUTÁNEAS LINEALES:
1.) PSORIASIS SEGMENTADA O LINEAL:
Hay muchos científicos que consideran al NEVIL como una variante
de la PSORIASIS, denominándola PSORIASIS LINEAL,
basados fundamentalmente en los hallazgos HISTOPATOLÓGICO (BIOPSIA) de las lesiones.
Por otra parte la PSORIASIS como todos ustedes saben es una
enfermedad multi factorial, que da signos y síntomas en otras aéreas
del cuerpo, y que tiende a recaer a menudo, relacionada con
VITILIGO y DIABETES. La mayoría de los niños con NEVIL o LIQUEN ESTRIADO que he
tratado NUNCA presentaron SIGNOS O SÍNTOMAS DE PSORIASIS, ni
recayeron, de modo que:
EL NEVIL Y EL LIQUEN ESTRIADO son totalmente diferentes a LA PSORIASIS LINEAL O SEGMENTADA, SON ENTIDADES DIFERENTES: La psoriasis lineal también sigue a las LINEAS DE BLASHCKO, pero clínicamente son las clásicas placas eritemato-escamosas TÍPICAS de la PSORIASIS; esta patología responde a tratamientos tópicos y sistémicos.
- Por cierto, NUNCA HE VISTO UN CASO DE "PSORIASIS LINEAL", en
niños ni adultos, existe como entidad, variante de la
PSORIASIS, pero no tiene nada que ver con el clásico NEVIL y LIQUEN ESTRIADO, que se
presenta en niño, y ocasionalmente en adultos.
2.) LIQUEN PLANO LINEAL:
LIQUEN PLANO LINEAL PIGMENTADO DEL CUELLO
3.) NEVUS SEBACEO LINEAL:
Esta lesión se presenta fundamentalmente en el cuero cabelludo, pero
también se puede presentar ocasionalmente en otras aéreas de la cara
descrito por primera vez por Josef Jadassohn, en 1895, medico Suizo alemán en conocido también como NEVUS SEBACEO DE JADASSOHN, es de aspecto verrugoso color pardo o anaranjado, congénito (está presente al
nacer), y su tratamiento es principalmente quirúrgico. (Ver foto)
NEVUS SEBACEO LINEAL (DE JADASSONHN)
4.) VITILIGO SEGMENTADO:
Es una variante del clásico vitiligo caracterizado por
maculas ACROMICAS (SIN COLOR) que aparecen en una metamera del cuerpo siguiendo las LINEAS DE BLASCHKO, son de mayor tamaño que las lesiones del
clásico LIQUEN ESTRIADO y NEVIL; puede presentarse en niños como adultos y el
tratamiento en estos casos es mas difícil pues la piel perdió la
coloración a nivel de los MELANOCITOS encargados de producir el pigmento o color de la piel.
5.) HERPES ZOSTER: (Virus de la Varicela-Zóster/VVZ)
EL HERPES ZOSTER, se presenta como un TRAYECTO LINEAL, rampante ("culebrilla"), el cual es adquirido, y producido por el virus de la VARICELA ZOSTER (VVZ), y la característica de las lesiones son ampollas y vesículas, acompañadas de prurito y dolor. Puede presentarse en cualquier area del cuerpo, incluyendo cuero cabelludo y mucosas (ojos), genitales.
- De modo que es totalmente diferente del LIQUEN ESTRIADO y NEVIL; la lesion desaparece con tratamiento medico, dejando en muchos casos un gran dolor, denominado NEURALGIA POST HERPETICA.(ACTUALIZACIÓN).
G.) CONCLUSIONES: si tu niño comienza a presentar lesiones dermatológicas en
forma de "LINEA" llévalo a la consulta dermatológica para establecer el
diagnostico adecuado y realizar un buen tratamiento.
Si eres adulto igualmente debes consultar a tu dermatólogo
- Repetimos: el LIQUEN ESTRIADO y EL NEVUS EPIDÉRMICO LINEAL (NEVIL), son muy parecidos.
Espero que esta revisión bibliográfica y fotos te orienten al
respecto.
Saludos a todos.
Dr. José M. Lapenta
EDITORIAL ENGLISH
===================
Hello friends of the DERMAGIC EXPRESS network today you I´m going
to talk about a very controversial topic and discussed today, THE LINEAR SKIN LESIONS in CHILDREN, specifically the
ILVEN whose initials stand for INFLAMMATORY LINEAR VERRUCOUS EPIDERMIC NEVUS, some scientists call it LICHEN STRIATUS, and others consider that
they are Different entities.
To clarify this controversy we are going to explain each one of them separately, their HISTORY, ETIOLOGY, EVOLUTION, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES and TREATMENTS:
1.) STRIATUS LICHEN:
A.) HISTORY:
This pathology was initially described in 1898 by two French dermatologists: François Henri Balzer and Lucien Marie François Mercier who gave it the name "trophoneurose lichenoid" in linear childhood cases.
- Subsequently in 1941, two American dermatologists: Francis Eugene Senear, and William Harry Caro, gave it the definitive name of "lichen striatus" (striated lichen), standardizing it clinically.
B.) ETIOLOGY:
1.) STRIATUS LICHEN:
A.) HISTORY:
This pathology was initially described in 1898 by two French dermatologists: François Henri Balzer and Lucien Marie François Mercier who gave it the name "trophoneurose lichenoid" in linear childhood cases.
- Subsequently in 1941, two American dermatologists: Francis Eugene Senear, and William Harry Caro, gave it the definitive name of "lichen striatus" (striated lichen), standardizing it clinically.
B.) ETIOLOGY:
- The cause is unknown (idiopathic), you usually find as background, NEVIC LESIONS (MOLES) in the ancestors of the affected.
- As the main theory of the appearance of STRIATUS LICHEN, a mechanism called GENETIC MOSAICISM is postulated, plus an ENVIRONMENTAL TRIGGER, that activates clones of anomalous skin cells, in the lines of Blaschko, generating a T-cell inflammatory response, causing a migration of keratinocytes towards those LINES OF BLASCHKO, with the consequent appearance of the lesions.
In S: in the abdomen.
In V: in the back.
In spiral form: Trunk.
Curved linears: arms and legs.
- These Lines were described for the first time in 1901, by the German Dermatologist Alfred Blaschko in the VII Congress of the German Dermatological Society, where he presented 140 cases of linear lesions.
"THE LINES OF BLASCHKO: They are invisible cutaneous patterns that represent trajectories of a clonal migration of epidermal cells that occurs during embryonic development (weeks 6-8 of gestation). They are imaginary lines product of a POSTZYGOTIC GENETIC MOSAICISM that follow the proliferation of TWO cell populations forming configurations depending on the body area, and do not correspond to dermatomes, nor to lymphatic vessels. Summarizing it is an embryonic cell migration."
In S: in the abdomen.
In V: in the back.
In spiral form: Trunk.
Curved linears: arms and legs.
- These Lines were described for the first time in 1901, by the German Dermatologist Alfred Blaschko in the VII Congress of the German Dermatological Society, where he presented 140 cases of linear lesions.
BLASCHKO'S LINES
In these IMAGINARY LINES, is where LICHEN STRIATUS, THE LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS NEVUS (ILVEN), and other linear pathologies such as LINEAR PSORIASIS, LINEAR LICHEN PLANUS, SEGMENTAL VITILIGO, and others like INCONTINENCE PIGMENTARY are expressed or manifested.
"THE DERMATOME: It is a specific area of skin sensorially innervated by a single spinal nerve (dorsal root of a medullary segment), example the CLASSIC HERPES ZOSTER (NOT LINEAR) and RECURRENT SIMPLE HERPES."
IDENTIFIED TRIGGERING FACTORS: in 20 to 50% of cases have been identified, as triggers:
a.- Minor traumas: Which would trigger the isomorphic phenomenon of Koebner): 15%.
b.- Viral infections: (varicella-zoster, EBV, CMV): 30%.
c.- Predisposing atopic dermatitis:50-61%: personal or family history.
e.- Vaccinations: doubtful aspect.
f.- Stress, medications, and contact dermatitis: Rare.
C.) CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- It is a rare dermatological condition that predominantly presents in children from 4 years onwards, with an average between 1 to 6 years; I have seen it appear in children a few months old.
- It presents in both males and females, with a predominance in males 2:1 over girls.
a.- Minor traumas: Which would trigger the isomorphic phenomenon of Koebner): 15%.
b.- Viral infections: (varicella-zoster, EBV, CMV): 30%.
c.- Predisposing atopic dermatitis:50-61%: personal or family history.
e.- Vaccinations: doubtful aspect.
f.- Stress, medications, and contact dermatitis: Rare.
C.) CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- It is a rare dermatological condition that predominantly presents in children from 4 years onwards, with an average between 1 to 6 years; I have seen it appear in children a few months old.
- It presents in both males and females, with a predominance in males 2:1 over girls.
- Basically the lesion is characterized by the SPONTANEOUS appearance of flat papules and plaques whose color can vary between hypochromia (no color) or pink and in some cases hyperpigmented, some with a verrucous appearance, which by temperature changes are "noticed" more.
- These spread in a "LINEAR" way following a metamer of the skin, called LINES OF BLASCHKO, until forming a kind of "PATH" or linear trajectory, completely asymptomatic or mildly pruritic, which Can present in neck, arms, legs, abdomen, peri-anal area, peri-vulvar, and in some cases the face.
- In some cases when LICHEN STRIATUS affects the tip of the finger there may be nail involvement: onycholysis, onychomadesis, sliptting. This occurs only in 5% of cases, and the lesions generally resolve spontaneously or with topical steroids.
- Most are totally asymptomatic but in some cases the only existing symptom is pruritus or itching and constitute a real headache, for the parents of these children who manifest this condition, mainly due to the aesthetic appearance.
"Parents who go to the consultation believe it is a "SHINGLES" due to the linear appearance of the lesion, and once the case is explained, they are TOTALLY SURPRISED that this type of disease exists in dermatology"
"Parents who go to the consultation believe it is a "SHINGLES" due to the linear appearance of the lesion, and once the case is explained, they are TOTALLY SURPRISED that this type of disease exists in dermatology"
D.) EVOLUTION:
LICHEN STRIATUS in its evolution, is SELF-LIMITED: The onset is generally acute begins to appear in days, with a peak of 1-3 months, until the appearance of the lesions stops.
- Then the resolution begins which is SPONTANEOUS, and can last between 6-12 months (average 9 months), leaving in some cases residual hypopigmentation (28%), or hyperpigmentation (8%), which disappears in 1-2 years. The resolution time decreases if appropriate treatments are applied.
- The pathology rarely relapses or recurs: it is said that 10% of cases; particularly I HAVE NOT SEEN RELAPSES in these cases.
E.) TREATMENTS:
There are several treatment options, which include:
A.- Topical corticosteroids.
B.- Tacrolimus.
C.- Pimecrolimus.
D.- Calcipotriol.
E. Triamcinolone.
F.- Tazarotene.
G.- Urea.
H. Salicylic acid.
THE CLASSIC LICHEN STRIATUS: DISAPPEARS with good dermatological treatment and a good percentage (70%) spontaneously.
G.) DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES:
There is a great controversy regarding these LINEAR LESIONS in children and adults and I am going to try to explain it to you as best as possible: The most common are:
1.) THE ILVEN OR LINEAR INFLAMMATORY EPIDERMAL NEVUS:
A.) HISTORY:
- This pathology was described for the first time in 1894 by the German dermatologist Paul Gerson Unna, one of the pioneers of cutaneous histopathology, who identified psoriasiform characteristics in linear epidermal nevi.
- In 1971, two American dermatologists: Altman and Mehregan, defined the term "LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (ILVEN)" after a series of 25 cases, differentiating it by intense inflammation, from other pathologies including STRIATUS LICHEN.
B.) ETIOLOGY:
LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (or ILVEN in English), has etiology similar to LICHEN STRIATUS: It is a GENETIC MOSAICISM, characterized by postzygotic mutations in KERATINOCYTES during embryogenesis (weeks 6-8), which causes a clonal hamartomatous proliferation, plus chronic inflammation. The altered chromosome is 15q.
- It is not hereditary in 99% of cases, considered sporadic acquired appearance, although some familial cases (mother-daughter) have been reported.
- As triggering factors have been reported: local trauma and HIV.
C.) CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- It is exactly the same in presentation and characteristics as LICHEN STRIATUS, in fact there are scientists as I mentioned at the beginning who consider both the same disease with different clinical expression.
- It presents in children and adolescents between 5 and 15 years and cases of presentation in adults have been described (5%); 75% of cases present before 7 years. 15% present between the 1st year of life and 5 years.
- Some authors consider the pathology of congenital nature.
- It is considered a variant of the EPIDERMAL NEVUS, and very SIMILAR in presentation to LICHEN STRIATUS, because like this one, it follows the LINES OF BLASCHKO. and the sites of appearance are the same as Lichen striatus: neck, arms, legs, abdomen, peri-anal area, peri-vulvar, and in some cases the face.
D.) EVOLUTION:
- The evolution of LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (ILVEN) is chronic and progressive, beginning in early childhood and persisting indefinitely without spontaneous remission, the verrucous lesions persist and treatment is needed to reduce their appearance, or make them disappear.
- There are cases of ILVEN where the papules or verrucous plaques DO NOT EXIST, but what gives it the characteristic of LINEAR EPIDERMAL INFLAMMATORY NEVUS is that the lesions WITHOUT treatment DO NOT DISAPPEAR, there is no spontaneous regression. Hypo-pigmented, hyperpigmented or achromic lesions remain for life.
B.) ETIOLOGY:
LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (or ILVEN in English), has etiology similar to LICHEN STRIATUS: It is a GENETIC MOSAICISM, characterized by postzygotic mutations in KERATINOCYTES during embryogenesis (weeks 6-8), which causes a clonal hamartomatous proliferation, plus chronic inflammation. The altered chromosome is 15q.
- It is not hereditary in 99% of cases, considered sporadic acquired appearance, although some familial cases (mother-daughter) have been reported.
- As triggering factors have been reported: local trauma and HIV.
C.) CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- It is exactly the same in presentation and characteristics as LICHEN STRIATUS, in fact there are scientists as I mentioned at the beginning who consider both the same disease with different clinical expression.
- It presents in children and adolescents between 5 and 15 years and cases of presentation in adults have been described (5%); 75% of cases present before 7 years. 15% present between the 1st year of life and 5 years.
- Some authors consider the pathology of congenital nature.
- It is considered a variant of the EPIDERMAL NEVUS, and very SIMILAR in presentation to LICHEN STRIATUS, because like this one, it follows the LINES OF BLASCHKO. and the sites of appearance are the same as Lichen striatus: neck, arms, legs, abdomen, peri-anal area, peri-vulvar, and in some cases the face.
D.) EVOLUTION:
- The evolution of LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (ILVEN) is chronic and progressive, beginning in early childhood and persisting indefinitely without spontaneous remission, the verrucous lesions persist and treatment is needed to reduce their appearance, or make them disappear.
- There are cases of ILVEN where the papules or verrucous plaques DO NOT EXIST, but what gives it the characteristic of LINEAR EPIDERMAL INFLAMMATORY NEVUS is that the lesions WITHOUT treatment DO NOT DISAPPEAR, there is no spontaneous regression. Hypo-pigmented, hyperpigmented or achromic lesions remain for life.
- This is one of the GREAT differences with LICHEN STRIATUS, which does present SPONTANEOUS REMISSION.
E.) TREATMENTS:
A.) Topical corticosteroids (40%): little effectiveness.
B.) Calcipotriol: (70%): partial control.
C.) CO2 LASER: (85%): definitive ablation.
D.) Systemic retinoids (60%): little use, only lightens the lesions.
F.) SUMMARY:
Both LICHEN STRIATUS and LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (ILVEN), are very similar in terms of appearance and clinical characteristics, but the great difference between both pathologies, is what we already discussed. LICHEN STRIATUS presents in the vast majority of cases with or without treatment SPONTANEOUS RESOLUTION, the LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS, does not present SPONTANEOUS REMISSION, it lasts a lifetime, unless treatment is done, AND EVEN SO, residual marks may remain.
E.) TREATMENTS:
A.) Topical corticosteroids (40%): little effectiveness.
B.) Calcipotriol: (70%): partial control.
C.) CO2 LASER: (85%): definitive ablation.
D.) Systemic retinoids (60%): little use, only lightens the lesions.
F.) SUMMARY:
Both LICHEN STRIATUS and LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (ILVEN), are very similar in terms of appearance and clinical characteristics, but the great difference between both pathologies, is what we already discussed. LICHEN STRIATUS presents in the vast majority of cases with or without treatment SPONTANEOUS RESOLUTION, the LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS, does not present SPONTANEOUS REMISSION, it lasts a lifetime, unless treatment is done, AND EVEN SO, residual marks may remain.
- Some authors consider both pathologies the same ENTITY with different clinical expression.
- Some scientists have described TOTAL disappearance of NEVIL with topical treatments; this fact raises the great question ? were they LICHEN STRIATUS ??
- Some scientists have described TOTAL disappearance of NEVIL with topical treatments; this fact raises the great question ? were they LICHEN STRIATUS ??
- Here I am going to tell you something based on MY EXPERIENCE: LICHEN STRIATUS , considered by some scientists as a variant of ILVEN (LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS NEVUS), when it disappears with good dermatological treatment, or spontaneously, DOES NOT REAPPEAR. I HAVE NEVER seen a LICHEN STRIATUS that was cured, reappear, or relapse.
LINEAR INFLAMMATORY VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS
THE LINEAR VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS: (NON INFLAMMATORY):
It is the CLASSIC ILVEN: a NEVIC lesion, mole type in LINE with VERRUCOUS appearance, (see photo), its coloration is light brown or hyperpigmented. As we said previously, the great difference is that this DOES NOT DISAPPEAR with conventional topical treatment and persists into adulthood. Other methods such as surgical excision or laser must be resorted to, most of them are congenital or appear in childhood.
LINEAR VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS BACK OF HAND
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS WITH OTHER LINEAR CUTANEOUS PATHOLOGIES:
1.) THE SEGMENTAL PSORIASIS (LINEAR):
There are many scientists who consider ILVEN as a variant of
PSORIASIS, denominating it LINEAR PSORIASIS, based
fundamentally on the HISTOPATHOLOGICAL (BIOPSY) findings of the
lesions.
Here I am going to tell you something based on
MY EXPERIENCE:
ILVEN (INFLAMMATORY LINEAR VERRUCOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS) it disappears with a good dermatological treatment and
DOES NOT REPEAT or REPLAPSE,
I have NEVER seen an
ILVEN that was cured to relapse
itself.
On the other hand the PSORIASIS as you all know is a multifactorial
disease that gives signs and symptoms in other areas of the body,
and that tends to relapse often, related to VITILIGO AND
DIABETES.
The majority of the children with ILVEN that I have tried NEVER presented SIGNS OR SYMPTOMS OF PSORIASIS, nor they relapse, so that...
The majority of the children with ILVEN that I have tried NEVER presented SIGNS OR SYMPTOMS OF PSORIASIS, nor they relapse, so that...
With great respect to scientists I say that
ILVEN AND
LINEAR OR SEGMENTAL PSORIASIS ARE DIFFERENT ENTITIES,
by the way, I have NEVER SEEN A CASE OF "LINEAR PSORIASIS", in
children or adults, it may exist as an entity, variant of PSORIASIS,
But it has nothing to do with the classic ILVEN that occurs in
children.
LINEAR SEGMENTAL PSORIASIS OF THE NECK
2.) LINEAR LICHEN PLANUS:
The LINEAR pigmentosus lichen planus is another entity that could be
confused with an ILVEN, but this usually occurs in adults and the
color of the lesion is usually a VIOLET or
BROWN
color,
LICHEN PLANUS UPADE 2025 which is highly PRURITIC, may appear on the face, highly related to
everyday stress. But just as ILVEN also disappears with a good
dermatological treatment. (View photo)
3.) SEBACEOUS LINEAR NEVUS:
===========================
This lesion occurs primarily in the scalp, but may also occur
occasionally in other areas of the face first described by Josef Jadassohn, a Swiss-German physician, in 1895, also known as SEBACEOUS NEVUS OF JADASSOHN, is
congenitally
brown or orange-colored (it is present at birth), and its treatment is primarily surgical.
(View photo)
4.) SEGMENTAL VITILIGO:
=======================
It is a variant of the classic vitiligo characterized by
ACROMIC macules (without COLOR) that appear in the body
following the lines of Blaschko, are of greater size than the
classic ILVEN lesions, can present in children as adults and the
treatment in these cases Is more difficult because the skin lost the
coloration at the level of the MELANOCYTES
responsible for producing the pigment or color of the skin.
5.) HERPES ZOSTER: (Varicella-Zoster Virus/VZV)
THE HERPES ZOSTER, presents as a LINEAR TRAJECTORY, rampaging ("shingles"), which is acquired, and produced by the VARICELLA ZOSTER virus (VZV), and the characteristic of the lesions are blisters and vesicles, accompanied by pruritus and pain. It can present in any area of the body, including scalp and mucous membranes (eyes), genitals.
THE HERPES ZOSTER, presents as a LINEAR TRAJECTORY, rampaging ("shingles"), which is acquired, and produced by the VARICELLA ZOSTER virus (VZV), and the characteristic of the lesions are blisters and vesicles, accompanied by pruritus and pain. It can present in any area of the body, including scalp and mucous membranes (eyes), genitals.
- So it is totally different from LICHEN STRIATUS and ILVEN; the lesion disappears with medical treatment, leaving in many cases great pain, called POST-HERPETIC NEURALGIA.(UPDATE).
CONCLUSION: if your
child begins to present dermatological lesions in the form of
"LINE" take it to the
dermatological consultation to establish the proper diagnosis and to
perform a good dermatological treatment. If you are an adult you
should also consult your dermatologist.
- We repeat: LICHEN STRIATUS and THE INFLAMMATORY LINEAR VERRUGOUS EPIDERMAL NEVUS (ILVEN), are very similar.
I hope this bibliographic review and photos guide you !
Greetings to all.
Dr. José Lapenta.
Dr. José M. Lapenta.
========================================================================
Dr. José M. Lapenta.
=======================================================================
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS/ BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES
=======================================================================
A.- Nail Lichen Striatus and Its Differential Diagnoses (2024).
B.- Lichen striatus: a review (2025).
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS/ BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES
=======================================================================
A.- Nail Lichen Striatus and Its Differential Diagnoses (2024).
B.- Lichen striatus: a review (2025).
=======================================================================
1.) ILVEN - COMPLETE REMISSION AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF TOPICAL
CORTICOSTEROID (CASE REVIEW).
2.) Successful treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus with tacrolimus and fluocinonide.
3.) Genital/Perigenital Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus: A Case Series.
4.) Does inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus represent a segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis?
5.) Immunohistochemical differentiation between inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) and psoriasis.
6.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus syndrome with its polymorphic presentation - A rare case report.
7.) Vulval and perianal inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus.
8.) Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
9.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
10.) Histopathologic varieties of epidermal nevus. A study of 160 cases.
11.) Inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus.
12.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus (ILVEN) versus linear psoriasis. A clinical, histological and immunohistochemical study.
13.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: why a combined laser therapy.14.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus and arthritis: a new association.
15.) [Successful therapy of an ILVEN in a 7-year-old girl with calcipotriol].
16.) Dithranol in the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
17.) Naevoid Psoriasis and ILVEN: Same Coin, Two Faces?
18.) Carbon dioxide laser treatment of epidermal nevi: response and long-term follow-up.
19.) A case of linear lichen planus pigmentosus.
20.) Lichen planus pigmentosus presenting in zosteriform pattern.
21.) Differential Diagnosis of Linear Eruptions in Children.
22.) Two cases of lichen striatus with prolonged active phase.
23.) Effective topical combination therapy for treatment of lichen striatus in children: a case series and review.
24.) [Lichen striatus with nail abnormality is a self-limiting condition].
================================================================ ================================================================
1.) ILVEN - COMPLETE REMISSION AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROID (CASE REVIEW).
===============================================================
Georgian Med News. 2017 Feb;(263):10-13.
Wollina U1, Tchernev G1.
Author information
1
Academic Teaching Hospital Dresden-Friedrichstadt, Department of Dermatology and Allergology; Medical Institute of Ministry of Interior (MVR), Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria.
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a relatively rare disorder with an onset at early age, consisting of pruritic linear papules and/or plaques and histologic features resembling psoriasis or lichenoid dermatitis. The disease is a version of mosaicism caused by somatic mutations. ILVEN belongs to the heterogeneous group of congenital hamartomas of embryonal ectodermal origin, as a variant of verrucous epidermal nevus, representing approximately 5% of all epidermal nevi, with predominance in females and with general therapeutic resistance. We report on an 18-month-old female patient with ILVEN, who failed to respond to topical tacrolimus, but achieved complete resolution with topical application of momethasone furoate 0.1% under occlusion for 2 weeks, with no signs of recurrence to date. Consequent topical therapy can provide excellent results in young children.
====================================================================
2.) Successful treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus with tacrolimus and fluocinonide.
====================================================================
Mutasim DF1.
J Cutan Med Surg. 2006 Jan-Feb;10(1):45-7.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH 45267-0592, USA. diya.mutasim@uc.edu
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a relatively rare disorder that is characterized by an early age at onset; severely pruritic linear papules and plaques; histologic features resembling spongiotic dermatitis, psoriasis, or lichenified dermatitis; and poor response to treatment.
OBJECTIVE:
To report the successful treatment of ILVEN with potent topical steroid and tacrolimus ointments.
METHODS:
An 11-year-old girl presented with a 1-year history of markedly pruritic, progressive linear eruption that extended from the right foot to the right buttock. She had failed treatment with pimecrolimus, calcipotriol, mometasone furoate, triamcinolone, tazarotene, and alpha-hydroxy acid. Histologic examination revealed the findings of spongiotic dermatitis.
RESULTS:
The lesions resolved with fluocinonide ointment and tacrolimus 0.1% ointment.
CONCLUSION:
The combination of two therapeutic agents with different mechanisms of action likely resulted in the successful treatment of this usually resistant condition.
====================================================================
3.) Genital/Perigenital Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus: A Case Series.
====================================================================
Indian J Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;60(6):592-5. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.169132.
Bandyopadhyay D1, Saha A1.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy, Medical College and Hospitals, Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a distinct variety of keratinocytic epidermal naevus. In contrast to non-inflammatory epidermal naevi, ILVEN are far less common, usually erythematous and intractably pruritic. ILVEN usually appears at birth or early childhood and has a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. Genital/perigenital involvement is relatively rare.
OBJECTIVES:
To describe the clinical features of 9 children with ILVEN localized to the genital and perigenital areas.
METHOD:
A retrospective study of 9 children with ILVEN presenting to a tertiary care Dermatology Clinic between 2007 and 2014 was undertaken. The clinical and histopathological features were reviewed.
RESULTS:
Nine children (6 females, 3 males) were included in the study based on their characteristic clinicopathological features. The lesions were associated with severe itching in all cases. The mean age at presentation was 4 years (range 1-11 years). Onset of lesions was before 6 months of age in 8 patients. Left sided involvement was twice as common as the right sided one. Male patients had penoscrotal and groin involvement while all the female children had vulvar lesions. None of the children had any extracutaneous abnormalities. The children were treated with topical agents with variable relief or symptoms.
CONCLUSIONS:
The possibility of ILVEN should be considered in every linear genital lesion in children. We have presented the largest series of perigenital ILVEN reported in English literature.
====================================================================
4.) Does inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus represent a segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis?
====================================================================
Dermatology. 2006;212(2):103-7.
Hofer T1.
Author information
1
Dermatology and Venereology FMH, Winkelriedstrasse 10, CH-5430 Wettingen, Switzerland. thomas.hofer@active.ch
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
A 6-year-old girl with a symmetric linear eruption on both of her legs, clinically and histologically resembling inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) or linear psoriasis (LP), with concomitant psoriasis of the guttata type and a positive family history of psoriasis is presented. The questions as to whether LP actually exists and ILVEN represents a distinct entity are still under debate.
OBJECTIVE AND METHODS:
The recent literature concerning case reports of ILVEN and LP is reviewed.
RESULTS:
Case reports of ILVEN and LP can be subdivided into four different groups: (1) ILVEN with or without concomitant psoriasis, only in part reacting to antipsoriatic treatment, (2) ILVEN without concomitant psoriasis, (3) LP with concomitant psoriasis vulgaris, with both groups 2 and 3 reacting successfully to antipsoriatic treatment, and (4) LP without concomitant psoriasis vulgaris and with no family history of psoriasis (very rarely reported).
CONCLUSION:
It is hypothesized that inflammatory linear verrucous eruption besides nevoid psoriasis/LP represents a further segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis which, if a (verrucous) epidermal nevus exists, shows a high affinity of occurrence in close context to such a nevus. Heritability is thought to be possible.
====================================================================
5.) Immunohistochemical differentiation between inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) and psoriasis.
====================================================================
Eur J Dermatol. 2004 Jul-Aug;14(4):216-20.
Vissers WH1, Muys L, Erp PE, de Jong EM, van de Kerkhof PC.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University Medical Centre St Radboud, P.O. Box 9101, 6500 HB Nijmegen, The Netherlands. w.vissers@derma.umcn.nl
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a rare skin disorder with a clinical and histological resemblance to psoriasis. In the past clinical and histological criteria have been defined. However, there remains a discussion as to whether ILVEN is a disease entity distinct from linear psoriasis. Our objective was to compare by quantitative immunohistochemistry the subsets of T-lymphocytes and markers for epidermal growth and keratinisation in biopsies taken from skin lesions of 4 patients with psoriasis and 3 patients with ILVEN: 1. patients with psoriasis (case 1-4) 2. patient with ILVEN cum psoriasis (case 5) 3. patients with ILVEN sine psoriasis (case 6 and 7). Our aim was to delineate ILVEN from psoriasis. Four patients with active psoriasis and three patients with signs and symptoms of ILVEN are described in this case report. Two patients of the ILVEN group had only linear verrucous lesions (ILVEN sine psoriasis), and one patient had linear lesions combined with widespread psoriasis outside the linear verrucous lesion (ILVEN cum psoriasis). The following markers were investigated in skin biopsies taken from the aforementioned patients by quantitative immunohistochemistry: CD2, CD4, CD8, CD25, CD161, CD94, CD45RO, CD45RA, HLA-DR, Keratin-10, Ki-67. In patients with ILVEN (cum and sine psoriasis) the number of Ki-67 positive nuclei, tended to be lower, the number of keratin-10 positive cells and HLA-DR expression higher as compared to psoriasis. In ILVEN sine psoriasis all T-cell subsets and cells expressing NK receptors were reduced as compared to psoriasis, except for CD45RA+ cells, whereas in the patient with ILVEN cum psoriasis the number of these T cell subsets had an intermediary position. In particular the density of CD8+, CD45RO+ and CD2+, CD94 and CD161 showed a marked difference between ILVEN sine psoriasis and psoriasis. In addition to the increased keratin 10 expression in ILVEN sine psoriasis, T cells relevant in the pathogenesis of psoriasis are markedly reduced in ILVEN sine psoriasis as compared to psoriasis. T-cell subsets in ILVEN cum psoriasis had an intermediary position.
====================================================================
6.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus syndrome with its polymorphic presentation - A rare case report.
====================================================================
Contemp Clin Dent. 2012 Jan;3(1):119-22. doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.94562.
Kumar CA1, Yeluri G, Raghav N.
Author information
1
Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, K. D. Dental College and Hospital, Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, India.
Abstract
Epidermal nevi are hamartomatous lesions that are typically present at birth, but can occur anytime during childhood and may rarely appear in adulthood. An estimated one-third of individuals with epidermal nevi have involvement of other organ systems; hence, this condition is considered to be an epidermal nevus syndrome. There are four distinct epidermal nevus syndromes recognizable by the different types of associated epithelial nevi: linear sebaceous nevi, linear nevus comedonicus, linear epidermal nevus, and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN). Each type may be regarded as a part of a syndrome with other systemic manifestations. We report a rare case of ILVEN syndrome in a 23-year-old female patient with a wide spectrum of mucosal, cutaneous, and skeletal abnormalities, demonstrating the polymorphic presentation of this condition.
====================================================================
7.) Vulval and perianal inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus.
====================================================================
Australas J Dermatol. 2009 May;50(2):115-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00518.x.
Le K1, Wong LC, Fischer G.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, The Children's Hospital at Westmead, Westmead, New South Wales, Australia. katie.le@unsw.edu.au
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus (ILVEN) is a rare form of epidermal naevus. It occurs as a linear dermatitic or psoriasiform plaque, with onset usually in the first 5 years of life. Lesions are characteristically intensely itchy. We present a case of ILVEN occurring on the vulva and perianal region of a 6-year-old girl. The lesion was initially thought to be an area of lichenified dermatitis; however, treatment with even super-potent topical corticosteroids did not significantly improve the inflammation. A biopsy was performed and histopathological examination showed characteristic features. ILVEN is frequently refractory to topical treatment and surgical excision of lesions may be an option for relief of symptoms. ILVEN occasionally presents in the inguinogenital region and in this area may, like many vulval naevi, be misdiagnosed as vulvitis, psoriasis, genital warts or sexual abuse.
====================================================================
8.) Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
J Dermatol. 1999 Sep;26(9):599-602.
Kawaguchi H1, Takeuchi M, Ono H, Nakajima H.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, Yokohama City University, School of Medicine, Japan.
Abstract
Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is reported in a 44-year-old Japanese man. A mild pruritic eruption appeared one year earlier and extended from the left dorsal foot to the gluteal region. Histologically, acanthosis and papillomatous thickening of epidermis as well as spongiotic edema and exocytosis with lymphocytes and neutrophils were observed. Topical tacalcitol was not effective, but the pruritus as well as the eruption slightly improved with topical corticosteroid and vaseline containing salicylic acid. This adult onset of ILVEN is considered to be a rare case.
====================================================================
9.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
====================================================================
Skoven I.
Abstract
A 12-year-old boy with inflammatory linear verrucous nevus is described. The lesions were pruritic and consisted of small, erythematous, slightly scaling papules coalescing to form linear, lichenified and excoriated plaques. The histological picture was psoriasiform but features of eczema were also seen.
====================================================================
10.) Histopathologic varieties of epidermal nevus. A study of 160 cases.
====================================================================
Am J Dermatopathol. 1982 Apr;4(2):161-70.
Su WP.
Abstract
The histopathologic features of 167 biopsy specimens from 160 patients with clinically typical epidermal nevi seen at the Mayo clinic between 1960 and 1978 were reviewed. The most common histopathologic pattern of epidermal nevus was hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges. Other histopathologic varieties of epidermal nevus included 1) acrokeratosis verruciformis-like, 2) epidermolytic hyperkeratosis, 3) seborrheic keratosis-like, 4)psoriasiform (inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus), 5) verrucoid, 6) porokeratosis-like, 7) focal acantholytic dyskeratosis, and 8) nevus comedonicus. Correlation of clinical and histopathologic findings is necessary in all lesions suspected of being epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
11.) Inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
Dermatologica. 1975;150(2):65-9.
Toribio JT, Quicres PA.
Abstract
A typical case of inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus (ILVEN), with quite a psoriasiform histologic pattern, is reported. Intralesionally administered paramethasone acetate caused a temporary suppression of the clinical and histopathologic inflammatory features. The concept of ILVEN is briefly discussed.
====================================================================
12.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus (ILVEN) versus linear psoriasis. A clinical, histological and immunohistochemical study.
====================================================================
de Jong E1, Rulo HF, van de Kerkhof PC.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
Abstract
Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus (ILVEN) has been suggested to be a separate disease entity. However, the distinction from linear psoriasis has been discussed in the literature over recent decades. The aim of the present study was to investigate, in addition to the clinical and histological criteria, the immunohistochemical aspects of inflammation, epidermal proliferation and keratinization. From a clinical and histological point of view, ILVEN and psoriasis, according to the established criteria, have been proved to overlap. The immunohistochemical study suggests that the following procedures have an additional diagnostic impact: assessment of elastase-positive cells, assessment of keratin 16 and of keratin 10.
====================================================================
13.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: why a combined laser therapy.
====================================================================
J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2013 Aug;15(4):242-5. doi: 10.3109/14764172.2013.807115. Epub 2013 Jun 21.
Conti R1, Bruscino N, Campolmi P, Bonan P, Cannarozzo G, Moretti S.
Author information
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, and more precisely an uncommon variant of the verrucous epidermal nevus. In our case report we describe an ILVEN female patient, resistant to previous treatments but responsive to a combined laser therapy, 10,600-nm CO2 laser and Fractional CO2 laser, with good and longstanding results. A complete resolution of the lesion was observed at the 9-month follow-up. The application of lasers has been reported in literature over recent years for resolving ILVEN lesions. Based on our clinical experience, 10,600-nm CO2 pulsed laser therapy seems to be the best treatment and Fractional CO2 laser treatment can be regarded as a very promising technique to combine with CO2 laser for reducing pigment modifications and endowing a more youthful appearance to the treated areas.
====================================================================
14.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus and arthritis: a new association.
===================================================================
J Pediatr. 2001 Apr;138(4):602-4.
Al-Enezi S1, Huber AM, Krafchik BR, Laxer RM.
Author information
1
Division of Rheumatology, Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a rare, chronic skin condition that begins in early childhood. We present two children with ILVEN and arthritis, a previously undescribed association. We discuss the relevance of this association and suggest appropriate management for this arthritis.
====================================================================
15.) [Successful therapy of an ILVEN in a 7-year-old girl with calcipotriol].
====================================================================
Hautarzt. 1999 Nov;50(11):812-4.
[Article in German]
Böhm I1, Bieber T, Bauer R.
Author information
1
Klinik und Poliklinik für Dermatologie der Rheinischen Friedrich-Wilhelms Universität Bonn.
Abstract
A 7-year-old otherwise healthy girl presented with a 2-year history of an ILVEN (inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus) located on the inner part of her right upper arm. The diagnosis was histologically confirmed. Different conservative therapeutic strategies with corticosteroids, antibiotics and antimycotics produced little or no improvement. Because of encouraging reports describing the successful use of 0.005% calcipotriol ointment in patients with ILVEN, we treated our patient with this regimen. After 4 weeks we could recognize a impressive improvement and after 8 weeks the ILVEN had nearly completely disappeared. 25 weeks after withdrawal of calcipotriol, no relapse had occurred. The dramatic response to calcipotriol suggests some pathological links between ILVEN and psoriasis.
====================================================================
16.) Dithranol in the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
Acta Derm Venereol. 1989;69(1):77-80.
de Mare S1, van de Kerkhof PC, Happle R.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
Abstract
A case of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is reported. Short contact treatment with dithranol resulted in complete relief from itching and a remarkable clearing of all linear lesions except from a small verrucous band on the shin. In patients with ILVEN it is advisable to try dithranol therapy before carrying out surgical procedures such as excision, cryotherapy, electrocautery. The prompt response to dithranol is best explained by the assumption that most of the lesions in this case of ILVEN represented true linear psoriasis.
====================================================================
17.) Naevoid Psoriasis and ILVEN: Same Coin, Two Faces?
====================================================================
Indian J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;57(6):489-91. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.103072.
Sengupta S1, Das JK, Gangopadhyay A.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, KPC Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata, India.
Abstract
The true existence of naevoid psoriasis and inflammatory linear verrucous naevus as distinct entities has been a debatable issue. Each has been opined to be a variant of the other. Considerable clinical and histological resemblance is seen between the two conditions. We describe three cases which attempt to throw more light on this issue.
====================================================================
18.) Carbon dioxide laser treatment of epidermal nevi: response and long-term follow-up.
====================================================================
Alonso-Castro L1, Boixeda P, Reig I, de Daniel-Rodríguez C, Fleta-Asín B, Jaén-Olasolo P.
Author information
1
Servicio de Dermatología, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, Madrid, Spain. letticiaac@gmail.com
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES:
Epidermal nevi, which are benign skin growths, have been treated using a range of approaches, with varying results. Topical treatments are ineffective and, while surgical excision is a more definitive treatment, it causes scar formation. In recent decades, epidermal nevi have been treated with various types of laser therapy. We describe our experience with the use of carbon dioxide (CO(2)) laser therapy to treat epidermal nevi and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevi (ILVEN).
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
Twenty patients (15 with epidermal nevi and 5 with ILVEN) underwent CO(2) laser treatment at our hospital between 2002 and 2010.
RESULTS:
Response was good (>50% reduction in lesion size) in 50% of cases and excellent (>75% reduction) in 30%. A greater resistance to treatment was observed in patients with ILVEN (only 40% had a good response). Long-term follow-up (at least 18 months) showed a recurrence rate of 30%. The side effects were hypopigmentation (25% of patients) and scarring (20%).
CONCLUSIONS:
We consider CO(2) laser therapy to be the treatment of choice for epidermal nevi as it is well tolerated and has proven to be safe and effective in the long term. While the response in patients with ILVEN was limited, CO(2) laser therapy might be a good option for selected cases or for palliative treatment since no other treatments have yet proven effective in this setting
====================================================================
19.) A case of linear lichen planus pigmentosus.
====================================================================
Ann Dermatol. 2010 Aug;22(3):323-5. doi: 10.5021/ad.2010.22.3.323. Epub 2010 Aug 5.
Seo JK1, Lee HJ, Lee D, Choi JH, Sung HS.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
Lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) is chronic pigmentary disorder that shows diffuse or reticulated hyperpigmented, dark brown macules on the sun-exposed areas such as the face, neck and other flexural folds. Clinically, it is different from classical lichen planus because LPP has a longer clinical course and it manifests with dark brown macules. In case of LPP, involvement of the scalp, nail or mucosal area is rare. The histopathological findings of the lesions show an atrophic epidermis, the presence of melanophages and a vacuolar alteration of the basal cell layer with a sparse lymphohistiocytic lichenoid infiltration. Although there have been a few reports of LPP, there have only 3 cases of linear LPP along the lines of Blaschko in the Korean dermatologic literature. Our patient had lesions on the neck and chin with a linear pattern. In this report, we describe a very rare case of LPP with a linear distribution related to Blaschko's lines on the neck and chin areas.
====================================================================
20.) Lichen planus pigmentosus presenting in zosteriform pattern.
====================================================================
Cho S1, Whang KK.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
Lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) has thus far been described as a condition of unknown etiology which clinically differs from the classical lichen planus (LP) by exhibiting dark brown macules and/or papules mostly in exposed areas and flexural folds and a longer clinical course without pruritus or scalp, nail or mucosal involvement. Histopathologically, LPP shows the typical changes seen in LP, but with thinning of epidermis. We report a case of LPP that developed in a unilateral, zosteriform pattern on the left flank of a 49-year-old man. This case seems to lie in the middle of the spectrum between classical LP and ashy dermatosis, and, to the best of our knowledge, is the first report of LPP presenting in the zosteriform pattern.
====================================================================
21.) Differential Diagnosis of Linear Eruptions in Children.
====================================================================
Kruse LL.
Abstract
A 3-year-old girl presented with a linear eruption on her leg for 2 months. She was otherwise healthy and well-appearing. Physical examination showed many small, erythematous, flat-topped papules coalescing into a linear erythematous plaque. At a follow-up visit 9 months later, the eruption had resolved, leaving postinflammatory hypopigmentation.When approaching a cutaneous eruption, appreciating the pattern of the lesions can be instrumental to arriving at the correct diagnosis. For this patient with the acute onset of a plaque on the leg, the differential diagnosis is narrowed by the linear distribution of the skin lesions. The differential diagnosis of linear eruptions in children includes lichen striatus, linear lichen planus, linear psoriasis, inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus, incontinentia pigmenti, phytophotodermatitis, and allergic contact dermatitis. Of note, many of these conditions manifest in a linear manner as a result of cutaneous mosaicism, whereas others are caused by external agents contacting the skin.
====================================================================
22.) Two cases of lichen striatus with prolonged active phase.
===================================================================
Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e67-8. doi: 10.1111/pde.12261. Epub 2014 Jan 24.
Feely MA1, Silverberg NB.
Author information
1
Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, NY; St. Luke's-Roosevelt Hospital Center, New York, NY.
Abstract
Lichen striatus is a localized, eczematous disorder distributed along the lines of Blaschko, primarily affecting children. In the literature, lesions have been described as having an active phase of inflamed lesions for 6 to 12 months followed by flattening and persistent pigmentary alteration. We describe two girls who had prolonged active-phase lesions for 2.5 and 3.5 years, respectively. Practitioners should be aware that lesions of lichen striatus may have a prolonged active phase.
====================================================================
23.) Effective topical combination therapy for treatment of lichen striatus in children: a case series and review.
====================================================================
Youssef SM1, Teng JM.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53715, USA.
Abstract
Lichen striatus (LS) is an uncommon linear dermatosis that is primarily seen in children from 4 months to 15 years of age. While some of these eruptions are asymptomatic, others can be quite pruritic. In darker-skinned individuals, post-inflammatory hypopigmentation can be significant and may provide a cause for concern for the patients and/or their parents. In our case series of 4 patients, we observed rapid resolution of LS by combining a topical retinoid with a topical steroid. To our knowledge, this is the first report of successful treatment with this kind of combination therapy in the English literature. The patients not only achieved satisfying cosmesis, but also complete resolution of their pruritus. The most common side effect of topical tazarotene is localized irritation at treatment sites, but the patients in this particular series tolerated the treatment well.
====================================================================
24.) [Lichen striatus with nail abnormality is a self-limiting condition].
====================================================================
Ugeskr Laeger. 2012 Mar 5;174(10):652-3.
[Article in Danish]
Sandreva T1, Bygum A.
Author information
1
Det Sundhedsvidenskabelige Fakultet, Syddansk Universitet, Campusvej 55, 5230 Odense, Denmark. tsand07@student.sdu.dk
Abstract
A six year-old boy was referred with an asymptomatic linear rash on his left arm and a nail involvement of a fingernail on his left hand. Multiple small erythematous papules coalescing into a linear band extending to the thumb with nail abnormality were noted on the left arm. A diagnosis of lichen striatus was established clinically. The condition has spontaneous remission, although the course of the disease is prolonged when nail involvement exists. The condition is benign and there is no need to perform biopsy.
2.) Successful treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus with tacrolimus and fluocinonide.
3.) Genital/Perigenital Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus: A Case Series.
4.) Does inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus represent a segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis?
5.) Immunohistochemical differentiation between inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) and psoriasis.
6.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus syndrome with its polymorphic presentation - A rare case report.
7.) Vulval and perianal inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus.
8.) Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
9.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
10.) Histopathologic varieties of epidermal nevus. A study of 160 cases.
11.) Inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus.
12.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus (ILVEN) versus linear psoriasis. A clinical, histological and immunohistochemical study.
13.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: why a combined laser therapy.14.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus and arthritis: a new association.
15.) [Successful therapy of an ILVEN in a 7-year-old girl with calcipotriol].
16.) Dithranol in the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
17.) Naevoid Psoriasis and ILVEN: Same Coin, Two Faces?
18.) Carbon dioxide laser treatment of epidermal nevi: response and long-term follow-up.
19.) A case of linear lichen planus pigmentosus.
20.) Lichen planus pigmentosus presenting in zosteriform pattern.
21.) Differential Diagnosis of Linear Eruptions in Children.
22.) Two cases of lichen striatus with prolonged active phase.
23.) Effective topical combination therapy for treatment of lichen striatus in children: a case series and review.
24.) [Lichen striatus with nail abnormality is a self-limiting condition].
================================================================ ================================================================
1.) ILVEN - COMPLETE REMISSION AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROID (CASE REVIEW).
===============================================================
Georgian Med News. 2017 Feb;(263):10-13.
Wollina U1, Tchernev G1.
Author information
1
Academic Teaching Hospital Dresden-Friedrichstadt, Department of Dermatology and Allergology; Medical Institute of Ministry of Interior (MVR), Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria.
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a relatively rare disorder with an onset at early age, consisting of pruritic linear papules and/or plaques and histologic features resembling psoriasis or lichenoid dermatitis. The disease is a version of mosaicism caused by somatic mutations. ILVEN belongs to the heterogeneous group of congenital hamartomas of embryonal ectodermal origin, as a variant of verrucous epidermal nevus, representing approximately 5% of all epidermal nevi, with predominance in females and with general therapeutic resistance. We report on an 18-month-old female patient with ILVEN, who failed to respond to topical tacrolimus, but achieved complete resolution with topical application of momethasone furoate 0.1% under occlusion for 2 weeks, with no signs of recurrence to date. Consequent topical therapy can provide excellent results in young children.
====================================================================
2.) Successful treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus with tacrolimus and fluocinonide.
====================================================================
Mutasim DF1.
J Cutan Med Surg. 2006 Jan-Feb;10(1):45-7.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH 45267-0592, USA. diya.mutasim@uc.edu
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a relatively rare disorder that is characterized by an early age at onset; severely pruritic linear papules and plaques; histologic features resembling spongiotic dermatitis, psoriasis, or lichenified dermatitis; and poor response to treatment.
OBJECTIVE:
To report the successful treatment of ILVEN with potent topical steroid and tacrolimus ointments.
METHODS:
An 11-year-old girl presented with a 1-year history of markedly pruritic, progressive linear eruption that extended from the right foot to the right buttock. She had failed treatment with pimecrolimus, calcipotriol, mometasone furoate, triamcinolone, tazarotene, and alpha-hydroxy acid. Histologic examination revealed the findings of spongiotic dermatitis.
RESULTS:
The lesions resolved with fluocinonide ointment and tacrolimus 0.1% ointment.
CONCLUSION:
The combination of two therapeutic agents with different mechanisms of action likely resulted in the successful treatment of this usually resistant condition.
====================================================================
3.) Genital/Perigenital Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus: A Case Series.
====================================================================
Indian J Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;60(6):592-5. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.169132.
Bandyopadhyay D1, Saha A1.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy, Medical College and Hospitals, Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a distinct variety of keratinocytic epidermal naevus. In contrast to non-inflammatory epidermal naevi, ILVEN are far less common, usually erythematous and intractably pruritic. ILVEN usually appears at birth or early childhood and has a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. Genital/perigenital involvement is relatively rare.
OBJECTIVES:
To describe the clinical features of 9 children with ILVEN localized to the genital and perigenital areas.
METHOD:
A retrospective study of 9 children with ILVEN presenting to a tertiary care Dermatology Clinic between 2007 and 2014 was undertaken. The clinical and histopathological features were reviewed.
RESULTS:
Nine children (6 females, 3 males) were included in the study based on their characteristic clinicopathological features. The lesions were associated with severe itching in all cases. The mean age at presentation was 4 years (range 1-11 years). Onset of lesions was before 6 months of age in 8 patients. Left sided involvement was twice as common as the right sided one. Male patients had penoscrotal and groin involvement while all the female children had vulvar lesions. None of the children had any extracutaneous abnormalities. The children were treated with topical agents with variable relief or symptoms.
CONCLUSIONS:
The possibility of ILVEN should be considered in every linear genital lesion in children. We have presented the largest series of perigenital ILVEN reported in English literature.
====================================================================
4.) Does inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus represent a segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis?
====================================================================
Dermatology. 2006;212(2):103-7.
Hofer T1.
Author information
1
Dermatology and Venereology FMH, Winkelriedstrasse 10, CH-5430 Wettingen, Switzerland. thomas.hofer@active.ch
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
A 6-year-old girl with a symmetric linear eruption on both of her legs, clinically and histologically resembling inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) or linear psoriasis (LP), with concomitant psoriasis of the guttata type and a positive family history of psoriasis is presented. The questions as to whether LP actually exists and ILVEN represents a distinct entity are still under debate.
OBJECTIVE AND METHODS:
The recent literature concerning case reports of ILVEN and LP is reviewed.
RESULTS:
Case reports of ILVEN and LP can be subdivided into four different groups: (1) ILVEN with or without concomitant psoriasis, only in part reacting to antipsoriatic treatment, (2) ILVEN without concomitant psoriasis, (3) LP with concomitant psoriasis vulgaris, with both groups 2 and 3 reacting successfully to antipsoriatic treatment, and (4) LP without concomitant psoriasis vulgaris and with no family history of psoriasis (very rarely reported).
CONCLUSION:
It is hypothesized that inflammatory linear verrucous eruption besides nevoid psoriasis/LP represents a further segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis which, if a (verrucous) epidermal nevus exists, shows a high affinity of occurrence in close context to such a nevus. Heritability is thought to be possible.
====================================================================
5.) Immunohistochemical differentiation between inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) and psoriasis.
====================================================================
Eur J Dermatol. 2004 Jul-Aug;14(4):216-20.
Vissers WH1, Muys L, Erp PE, de Jong EM, van de Kerkhof PC.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University Medical Centre St Radboud, P.O. Box 9101, 6500 HB Nijmegen, The Netherlands. w.vissers@derma.umcn.nl
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a rare skin disorder with a clinical and histological resemblance to psoriasis. In the past clinical and histological criteria have been defined. However, there remains a discussion as to whether ILVEN is a disease entity distinct from linear psoriasis. Our objective was to compare by quantitative immunohistochemistry the subsets of T-lymphocytes and markers for epidermal growth and keratinisation in biopsies taken from skin lesions of 4 patients with psoriasis and 3 patients with ILVEN: 1. patients with psoriasis (case 1-4) 2. patient with ILVEN cum psoriasis (case 5) 3. patients with ILVEN sine psoriasis (case 6 and 7). Our aim was to delineate ILVEN from psoriasis. Four patients with active psoriasis and three patients with signs and symptoms of ILVEN are described in this case report. Two patients of the ILVEN group had only linear verrucous lesions (ILVEN sine psoriasis), and one patient had linear lesions combined with widespread psoriasis outside the linear verrucous lesion (ILVEN cum psoriasis). The following markers were investigated in skin biopsies taken from the aforementioned patients by quantitative immunohistochemistry: CD2, CD4, CD8, CD25, CD161, CD94, CD45RO, CD45RA, HLA-DR, Keratin-10, Ki-67. In patients with ILVEN (cum and sine psoriasis) the number of Ki-67 positive nuclei, tended to be lower, the number of keratin-10 positive cells and HLA-DR expression higher as compared to psoriasis. In ILVEN sine psoriasis all T-cell subsets and cells expressing NK receptors were reduced as compared to psoriasis, except for CD45RA+ cells, whereas in the patient with ILVEN cum psoriasis the number of these T cell subsets had an intermediary position. In particular the density of CD8+, CD45RO+ and CD2+, CD94 and CD161 showed a marked difference between ILVEN sine psoriasis and psoriasis. In addition to the increased keratin 10 expression in ILVEN sine psoriasis, T cells relevant in the pathogenesis of psoriasis are markedly reduced in ILVEN sine psoriasis as compared to psoriasis. T-cell subsets in ILVEN cum psoriasis had an intermediary position.
====================================================================
6.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus syndrome with its polymorphic presentation - A rare case report.
====================================================================
Contemp Clin Dent. 2012 Jan;3(1):119-22. doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.94562.
Kumar CA1, Yeluri G, Raghav N.
Author information
1
Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, K. D. Dental College and Hospital, Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, India.
Abstract
Epidermal nevi are hamartomatous lesions that are typically present at birth, but can occur anytime during childhood and may rarely appear in adulthood. An estimated one-third of individuals with epidermal nevi have involvement of other organ systems; hence, this condition is considered to be an epidermal nevus syndrome. There are four distinct epidermal nevus syndromes recognizable by the different types of associated epithelial nevi: linear sebaceous nevi, linear nevus comedonicus, linear epidermal nevus, and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN). Each type may be regarded as a part of a syndrome with other systemic manifestations. We report a rare case of ILVEN syndrome in a 23-year-old female patient with a wide spectrum of mucosal, cutaneous, and skeletal abnormalities, demonstrating the polymorphic presentation of this condition.
====================================================================
7.) Vulval and perianal inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus.
====================================================================
Australas J Dermatol. 2009 May;50(2):115-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00518.x.
Le K1, Wong LC, Fischer G.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, The Children's Hospital at Westmead, Westmead, New South Wales, Australia. katie.le@unsw.edu.au
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus (ILVEN) is a rare form of epidermal naevus. It occurs as a linear dermatitic or psoriasiform plaque, with onset usually in the first 5 years of life. Lesions are characteristically intensely itchy. We present a case of ILVEN occurring on the vulva and perianal region of a 6-year-old girl. The lesion was initially thought to be an area of lichenified dermatitis; however, treatment with even super-potent topical corticosteroids did not significantly improve the inflammation. A biopsy was performed and histopathological examination showed characteristic features. ILVEN is frequently refractory to topical treatment and surgical excision of lesions may be an option for relief of symptoms. ILVEN occasionally presents in the inguinogenital region and in this area may, like many vulval naevi, be misdiagnosed as vulvitis, psoriasis, genital warts or sexual abuse.
====================================================================
8.) Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
J Dermatol. 1999 Sep;26(9):599-602.
Kawaguchi H1, Takeuchi M, Ono H, Nakajima H.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, Yokohama City University, School of Medicine, Japan.
Abstract
Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is reported in a 44-year-old Japanese man. A mild pruritic eruption appeared one year earlier and extended from the left dorsal foot to the gluteal region. Histologically, acanthosis and papillomatous thickening of epidermis as well as spongiotic edema and exocytosis with lymphocytes and neutrophils were observed. Topical tacalcitol was not effective, but the pruritus as well as the eruption slightly improved with topical corticosteroid and vaseline containing salicylic acid. This adult onset of ILVEN is considered to be a rare case.
====================================================================
9.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
====================================================================
Skoven I.
Abstract
A 12-year-old boy with inflammatory linear verrucous nevus is described. The lesions were pruritic and consisted of small, erythematous, slightly scaling papules coalescing to form linear, lichenified and excoriated plaques. The histological picture was psoriasiform but features of eczema were also seen.
====================================================================
10.) Histopathologic varieties of epidermal nevus. A study of 160 cases.
====================================================================
Am J Dermatopathol. 1982 Apr;4(2):161-70.
Su WP.
Abstract
The histopathologic features of 167 biopsy specimens from 160 patients with clinically typical epidermal nevi seen at the Mayo clinic between 1960 and 1978 were reviewed. The most common histopathologic pattern of epidermal nevus was hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges. Other histopathologic varieties of epidermal nevus included 1) acrokeratosis verruciformis-like, 2) epidermolytic hyperkeratosis, 3) seborrheic keratosis-like, 4)psoriasiform (inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus), 5) verrucoid, 6) porokeratosis-like, 7) focal acantholytic dyskeratosis, and 8) nevus comedonicus. Correlation of clinical and histopathologic findings is necessary in all lesions suspected of being epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
11.) Inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
Dermatologica. 1975;150(2):65-9.
Toribio JT, Quicres PA.
Abstract
A typical case of inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus (ILVEN), with quite a psoriasiform histologic pattern, is reported. Intralesionally administered paramethasone acetate caused a temporary suppression of the clinical and histopathologic inflammatory features. The concept of ILVEN is briefly discussed.
====================================================================
12.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus (ILVEN) versus linear psoriasis. A clinical, histological and immunohistochemical study.
====================================================================
de Jong E1, Rulo HF, van de Kerkhof PC.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
Abstract
Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus (ILVEN) has been suggested to be a separate disease entity. However, the distinction from linear psoriasis has been discussed in the literature over recent decades. The aim of the present study was to investigate, in addition to the clinical and histological criteria, the immunohistochemical aspects of inflammation, epidermal proliferation and keratinization. From a clinical and histological point of view, ILVEN and psoriasis, according to the established criteria, have been proved to overlap. The immunohistochemical study suggests that the following procedures have an additional diagnostic impact: assessment of elastase-positive cells, assessment of keratin 16 and of keratin 10.
====================================================================
13.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: why a combined laser therapy.
====================================================================
J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2013 Aug;15(4):242-5. doi: 10.3109/14764172.2013.807115. Epub 2013 Jun 21.
Conti R1, Bruscino N, Campolmi P, Bonan P, Cannarozzo G, Moretti S.
Author information
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, and more precisely an uncommon variant of the verrucous epidermal nevus. In our case report we describe an ILVEN female patient, resistant to previous treatments but responsive to a combined laser therapy, 10,600-nm CO2 laser and Fractional CO2 laser, with good and longstanding results. A complete resolution of the lesion was observed at the 9-month follow-up. The application of lasers has been reported in literature over recent years for resolving ILVEN lesions. Based on our clinical experience, 10,600-nm CO2 pulsed laser therapy seems to be the best treatment and Fractional CO2 laser treatment can be regarded as a very promising technique to combine with CO2 laser for reducing pigment modifications and endowing a more youthful appearance to the treated areas.
====================================================================
14.) Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus and arthritis: a new association.
===================================================================
J Pediatr. 2001 Apr;138(4):602-4.
Al-Enezi S1, Huber AM, Krafchik BR, Laxer RM.
Author information
1
Division of Rheumatology, Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Abstract
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a rare, chronic skin condition that begins in early childhood. We present two children with ILVEN and arthritis, a previously undescribed association. We discuss the relevance of this association and suggest appropriate management for this arthritis.
====================================================================
15.) [Successful therapy of an ILVEN in a 7-year-old girl with calcipotriol].
====================================================================
Hautarzt. 1999 Nov;50(11):812-4.
[Article in German]
Böhm I1, Bieber T, Bauer R.
Author information
1
Klinik und Poliklinik für Dermatologie der Rheinischen Friedrich-Wilhelms Universität Bonn.
Abstract
A 7-year-old otherwise healthy girl presented with a 2-year history of an ILVEN (inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus) located on the inner part of her right upper arm. The diagnosis was histologically confirmed. Different conservative therapeutic strategies with corticosteroids, antibiotics and antimycotics produced little or no improvement. Because of encouraging reports describing the successful use of 0.005% calcipotriol ointment in patients with ILVEN, we treated our patient with this regimen. After 4 weeks we could recognize a impressive improvement and after 8 weeks the ILVEN had nearly completely disappeared. 25 weeks after withdrawal of calcipotriol, no relapse had occurred. The dramatic response to calcipotriol suggests some pathological links between ILVEN and psoriasis.
====================================================================
16.) Dithranol in the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus.
====================================================================
Acta Derm Venereol. 1989;69(1):77-80.
de Mare S1, van de Kerkhof PC, Happle R.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
Abstract
A case of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is reported. Short contact treatment with dithranol resulted in complete relief from itching and a remarkable clearing of all linear lesions except from a small verrucous band on the shin. In patients with ILVEN it is advisable to try dithranol therapy before carrying out surgical procedures such as excision, cryotherapy, electrocautery. The prompt response to dithranol is best explained by the assumption that most of the lesions in this case of ILVEN represented true linear psoriasis.
====================================================================
17.) Naevoid Psoriasis and ILVEN: Same Coin, Two Faces?
====================================================================
Indian J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;57(6):489-91. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.103072.
Sengupta S1, Das JK, Gangopadhyay A.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, KPC Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata, India.
Abstract
The true existence of naevoid psoriasis and inflammatory linear verrucous naevus as distinct entities has been a debatable issue. Each has been opined to be a variant of the other. Considerable clinical and histological resemblance is seen between the two conditions. We describe three cases which attempt to throw more light on this issue.
====================================================================
18.) Carbon dioxide laser treatment of epidermal nevi: response and long-term follow-up.
====================================================================
Alonso-Castro L1, Boixeda P, Reig I, de Daniel-Rodríguez C, Fleta-Asín B, Jaén-Olasolo P.
Author information
1
Servicio de Dermatología, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, Madrid, Spain. letticiaac@gmail.com
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES:
Epidermal nevi, which are benign skin growths, have been treated using a range of approaches, with varying results. Topical treatments are ineffective and, while surgical excision is a more definitive treatment, it causes scar formation. In recent decades, epidermal nevi have been treated with various types of laser therapy. We describe our experience with the use of carbon dioxide (CO(2)) laser therapy to treat epidermal nevi and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevi (ILVEN).
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
Twenty patients (15 with epidermal nevi and 5 with ILVEN) underwent CO(2) laser treatment at our hospital between 2002 and 2010.
RESULTS:
Response was good (>50% reduction in lesion size) in 50% of cases and excellent (>75% reduction) in 30%. A greater resistance to treatment was observed in patients with ILVEN (only 40% had a good response). Long-term follow-up (at least 18 months) showed a recurrence rate of 30%. The side effects were hypopigmentation (25% of patients) and scarring (20%).
CONCLUSIONS:
We consider CO(2) laser therapy to be the treatment of choice for epidermal nevi as it is well tolerated and has proven to be safe and effective in the long term. While the response in patients with ILVEN was limited, CO(2) laser therapy might be a good option for selected cases or for palliative treatment since no other treatments have yet proven effective in this setting
====================================================================
19.) A case of linear lichen planus pigmentosus.
====================================================================
Ann Dermatol. 2010 Aug;22(3):323-5. doi: 10.5021/ad.2010.22.3.323. Epub 2010 Aug 5.
Seo JK1, Lee HJ, Lee D, Choi JH, Sung HS.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
Lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) is chronic pigmentary disorder that shows diffuse or reticulated hyperpigmented, dark brown macules on the sun-exposed areas such as the face, neck and other flexural folds. Clinically, it is different from classical lichen planus because LPP has a longer clinical course and it manifests with dark brown macules. In case of LPP, involvement of the scalp, nail or mucosal area is rare. The histopathological findings of the lesions show an atrophic epidermis, the presence of melanophages and a vacuolar alteration of the basal cell layer with a sparse lymphohistiocytic lichenoid infiltration. Although there have been a few reports of LPP, there have only 3 cases of linear LPP along the lines of Blaschko in the Korean dermatologic literature. Our patient had lesions on the neck and chin with a linear pattern. In this report, we describe a very rare case of LPP with a linear distribution related to Blaschko's lines on the neck and chin areas.
====================================================================
20.) Lichen planus pigmentosus presenting in zosteriform pattern.
====================================================================
Cho S1, Whang KK.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
Lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) has thus far been described as a condition of unknown etiology which clinically differs from the classical lichen planus (LP) by exhibiting dark brown macules and/or papules mostly in exposed areas and flexural folds and a longer clinical course without pruritus or scalp, nail or mucosal involvement. Histopathologically, LPP shows the typical changes seen in LP, but with thinning of epidermis. We report a case of LPP that developed in a unilateral, zosteriform pattern on the left flank of a 49-year-old man. This case seems to lie in the middle of the spectrum between classical LP and ashy dermatosis, and, to the best of our knowledge, is the first report of LPP presenting in the zosteriform pattern.
====================================================================
21.) Differential Diagnosis of Linear Eruptions in Children.
====================================================================
Kruse LL.
Abstract
A 3-year-old girl presented with a linear eruption on her leg for 2 months. She was otherwise healthy and well-appearing. Physical examination showed many small, erythematous, flat-topped papules coalescing into a linear erythematous plaque. At a follow-up visit 9 months later, the eruption had resolved, leaving postinflammatory hypopigmentation.When approaching a cutaneous eruption, appreciating the pattern of the lesions can be instrumental to arriving at the correct diagnosis. For this patient with the acute onset of a plaque on the leg, the differential diagnosis is narrowed by the linear distribution of the skin lesions. The differential diagnosis of linear eruptions in children includes lichen striatus, linear lichen planus, linear psoriasis, inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus, incontinentia pigmenti, phytophotodermatitis, and allergic contact dermatitis. Of note, many of these conditions manifest in a linear manner as a result of cutaneous mosaicism, whereas others are caused by external agents contacting the skin.
====================================================================
22.) Two cases of lichen striatus with prolonged active phase.
===================================================================
Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e67-8. doi: 10.1111/pde.12261. Epub 2014 Jan 24.
Feely MA1, Silverberg NB.
Author information
1
Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, NY; St. Luke's-Roosevelt Hospital Center, New York, NY.
Abstract
Lichen striatus is a localized, eczematous disorder distributed along the lines of Blaschko, primarily affecting children. In the literature, lesions have been described as having an active phase of inflamed lesions for 6 to 12 months followed by flattening and persistent pigmentary alteration. We describe two girls who had prolonged active-phase lesions for 2.5 and 3.5 years, respectively. Practitioners should be aware that lesions of lichen striatus may have a prolonged active phase.
====================================================================
23.) Effective topical combination therapy for treatment of lichen striatus in children: a case series and review.
====================================================================
Youssef SM1, Teng JM.
Author information
1
Department of Dermatology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53715, USA.
Abstract
Lichen striatus (LS) is an uncommon linear dermatosis that is primarily seen in children from 4 months to 15 years of age. While some of these eruptions are asymptomatic, others can be quite pruritic. In darker-skinned individuals, post-inflammatory hypopigmentation can be significant and may provide a cause for concern for the patients and/or their parents. In our case series of 4 patients, we observed rapid resolution of LS by combining a topical retinoid with a topical steroid. To our knowledge, this is the first report of successful treatment with this kind of combination therapy in the English literature. The patients not only achieved satisfying cosmesis, but also complete resolution of their pruritus. The most common side effect of topical tazarotene is localized irritation at treatment sites, but the patients in this particular series tolerated the treatment well.
====================================================================
24.) [Lichen striatus with nail abnormality is a self-limiting condition].
====================================================================
Ugeskr Laeger. 2012 Mar 5;174(10):652-3.
[Article in Danish]
Sandreva T1, Bygum A.
Author information
1
Det Sundhedsvidenskabelige Fakultet, Syddansk Universitet, Campusvej 55, 5230 Odense, Denmark. tsand07@student.sdu.dk
Abstract
A six year-old boy was referred with an asymptomatic linear rash on his left arm and a nail involvement of a fingernail on his left hand. Multiple small erythematous papules coalescing into a linear band extending to the thumb with nail abnormality were noted on the left arm. A diagnosis of lichen striatus was established clinically. The condition has spontaneous remission, although the course of the disease is prolonged when nail involvement exists. The condition is benign and there is no need to perform biopsy.
Producido Por Dr. Jose Lapenta R. Dermatologo
Maracay Estado Aragua Venezuela 2.025
Telf: 04142976087- 04127766810
04243431100
Follow @dermagicexpress






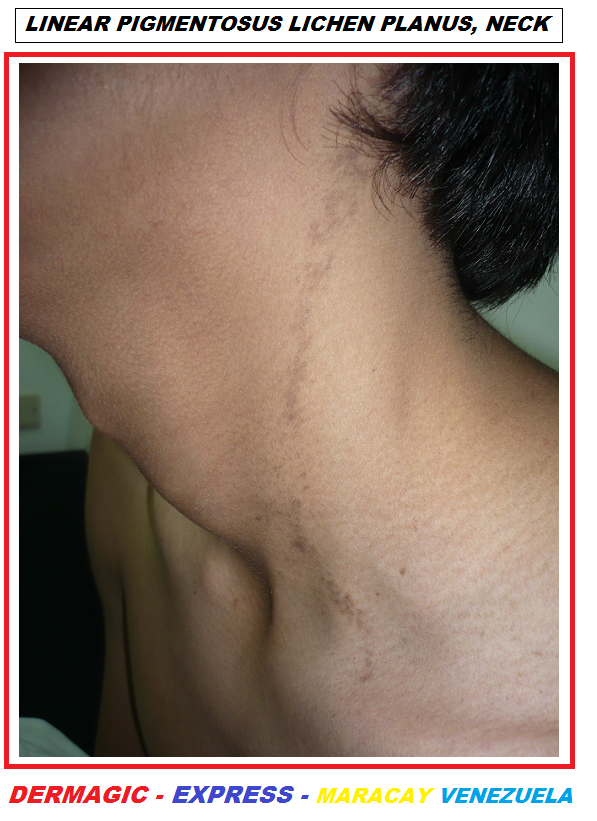







No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario
Tu comentario será objeto de revisión y luego aprobado.
Your comment will be revised and then approved.